
Diatomaceous earth is a type of sand made from the fossilized remains of aquatic (water-living) organisms called diatoms. Their skeletons are made up of silica, which is deposited in riverbeds and at the bottom of streams, lakes, and oceans. (1)

Diatomaceous earth is used as a natural pesticide; its sharp edges absorb oils and fat from pests, killing them. (1)
Diatomaceous earth is available for edible use after purification. The National Food and Drug Administration recognizes it as “food grade” and is used as an anticaking agent in animal feeds or clarifying agent in alcoholic beverages. (1)
Diatomaceous earth is a versatile material and can be used in many ways.
AdvertisementsDiatomaceous earth can be used as a household pest control against bed bugs, cockroaches, mosquitoes, and termites. (2)
It works by causing abrasive wounds to the pests or absorbing oils and water from their bodies depending on the shape of the diatoms. (2) This provides a safe, toxic-free way to deal with household pests.
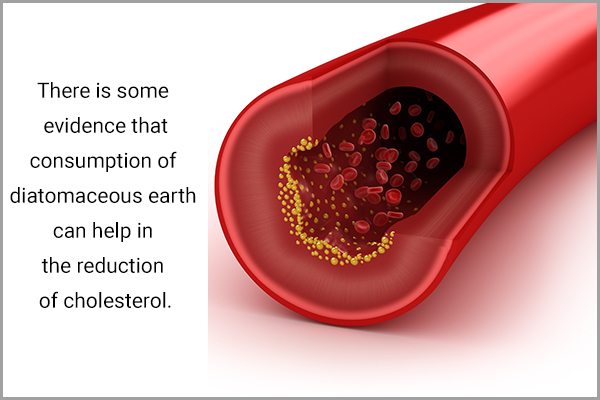
There is some evidence that consumption of diatomaceous earth can help in the reduction of cholesterol levels.
One study observed that taking 250 mg of diatomaceous earth three times a day reduced the levels of total cholesterol, LDL (bad cholesterol), and triglycerides. (3)
While the findings of this study are positive, more recent human studies are needed to establish the efficacy of diatomaceous earth in reducing cholesterol levels.
During the second wave of COVID-19 in South Asia in 2021, there was an increased incidence of fungal infections. Studies found that a combination of diatomaceous earth and zinc oxide showed a strong antibiotic action against fungi and bacteria such as E. coli and S. enterica. (4)
AdvertisementsThe combination had three times lesser toxicity than commercially available silicon dioxide and zinc oxide combinations. It also reduced the need for additional doses of antifungal agents by improving the action capacity of a single dose. (4)
This could be potentially useful research in the enhancement of antibiotic and antifungal medication.

Many people exposed to house dust mites may exhibit symptoms of asthma. Thus, people suffering from asthma may benefit from reducing potential allergens in the environment such as house dust mites. (5)
Sprinkling diatomaceous earth in the environment or homes can reduce the inflammation and allergic response caused by dust mites, proving to be a potentially useful agent in the management of asthma. (5)
Diatomaceous earth has a rich amount of silica/silicon, (6) which is useful in managing many health conditions, although more research is needed on the advantages of diatomaceous earth and its silica content on health.
In addition to calcium and vitamin D, silicon is also important in improving the mineral density of bones and increasing bone strength. These effects are potentially useful for postmenopausal women with an increased risk of osteoporosis. (7)
AdvertisementsFoods rich in silicon include cereals, whole grains, and green beans and can be included in the diet. (7)
Silicon is important in the synthesis of collagen, which is the main component of nails, hair, and skin. It improves skin elasticity and strength. (8) It also reduces hair loss, improves hair shine, and could be useful in managing premature balding. (8)
Some studies have established the role of aluminum toxicity in worsening the symptoms of Alzheimer’s. Silica can clear excess aluminum from the body, thereby improving the brain’s function and performance in some people. (9)
However, the study did not make use of diatomaceous earth, so it is unclear if the same results will be observed with diatomaceous earth.
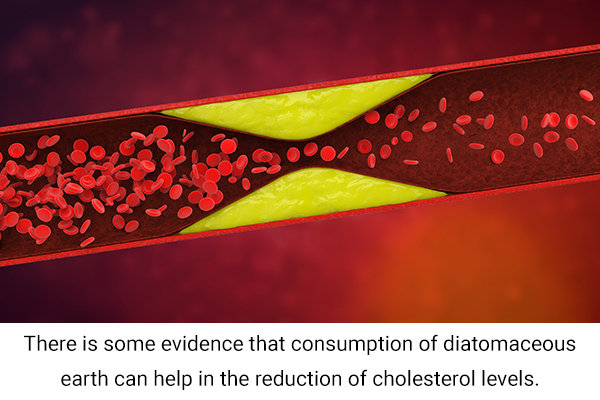
Silicon in the diet plays a protective role in blood vessels. If the cholesterol-reducing action of diatomaceous earth due to its silica content is to be believed, then it may also help in reducing the incidence of atherosclerosis. (10) However, in animal models, silicon showed no impact on reducing atherosclerosis development.
Diatoms – the organisms that diatomaceous earth is made from – are rich in fatty acids, proteins, flavonoids, sterols, etc., which have been found to have antioxidant and anticancer properties. The silica in diatoms is also effective in increasing the potency of anticancer medication. (11)
It is important to remember that there are many other natural foods with possible anticancer activities that can also be consumed.
AdvertisementsBefore you consider using diatomaceous earth for any benefits to the body, remember that there is no current evidence for its benefits for health. Moreover, the high silica content of diatomaceous earth can lead to toxicity and respiratory issues. (6)
When using diatomaceous earth for ridding the homes of pests, take the following precautions: (12)

As it is a powder, it is not likely to lose its potency and works for a long time in killing pests.
Small amounts of diatomaceous earth can safely pass through the intestine. However, its consumption is associated with a risk of toxicity; in such a case, it is recommended to consult a physician immediately.
AdvertisementsDiatomaceous earth is the fossilized remains of algae and small marine animals. It is used as a natural pesticide to kill household pests.
There are some benefits attached to the consumption of diatomaceous earth such as improving skin, hair, and nail health, reducing cholesterol levels, improving bone remineralization, and also possibly reducing cognitive decline in degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
However, there is a risk associated with the consumption of diatomaceous earth, and precaution must be taken with its use.